Development of New Synthetic Method and Strategy
- Stereospecific 1,2-rearrangement
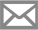
- Pinacol-type rearrangement
- Epoxy alcohol-aldol rearrangement
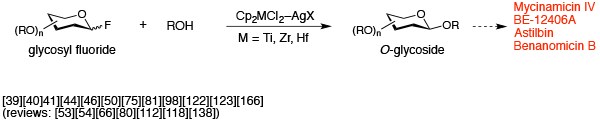
- Highly efficient glycosidation (metallocene method)
- Cyclopropane formation
- New efficient method for “benzyne” generation
- Cycloadditions of benzyne
- Aryl C-glycosidation reaction (O→C-glycoside rearrangement)
- Chemistry of strained molecules 1
- Double bond insertion (C=O)
- Double Bond insertion (C=C)
- Oxygene insertion (synthesis of phthalides)
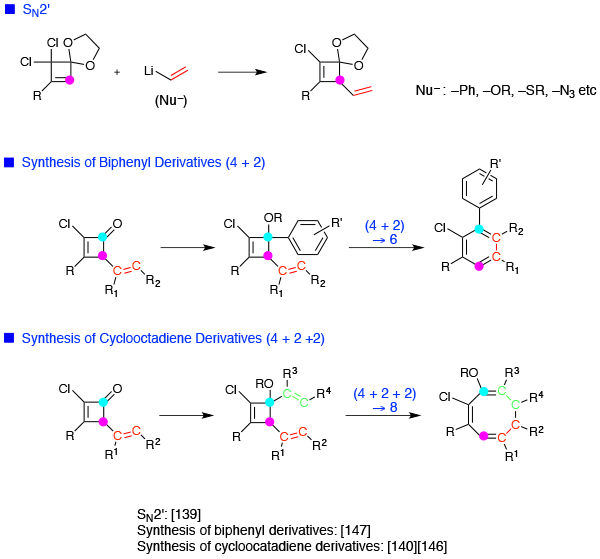
- Chemistry of Strained molecules 2
- SN2′ reaction
- Synthesis of biphenyl derivatives ([4+2])
- Synthesis of cyclooctadiene derivatives ([4+2+2])
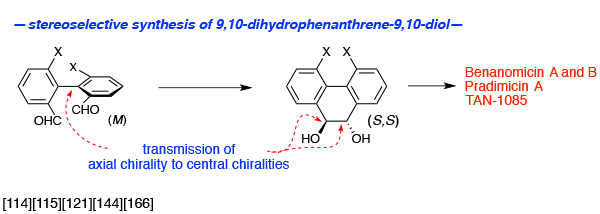
- Pinacol cyclization
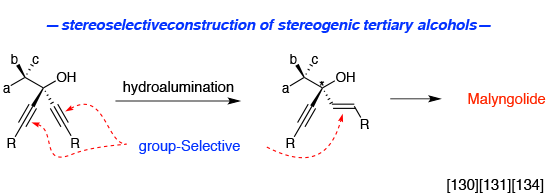
- Group-selective hydroalumination
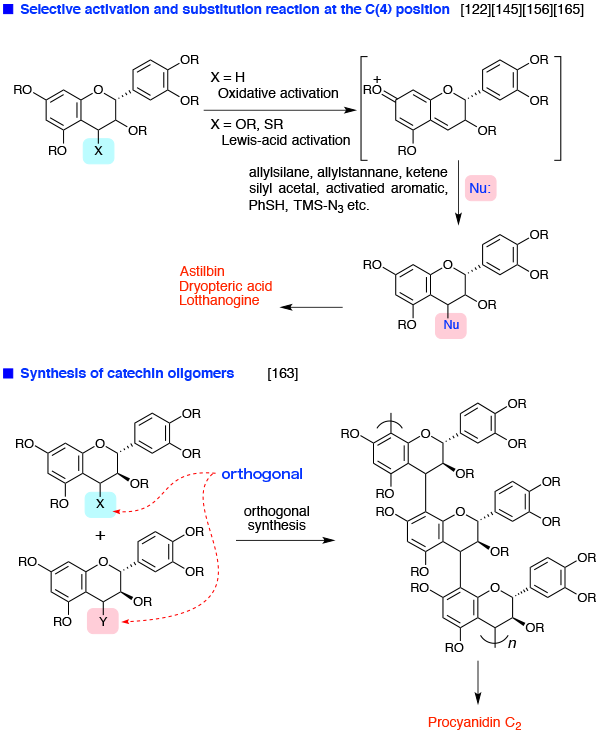
- Chemistry of flavonoids
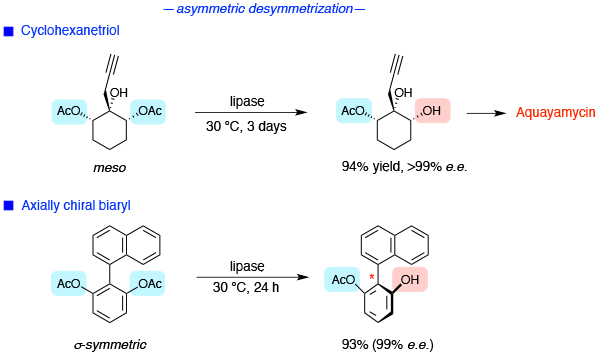
- Enzyme-catalyzed reactions
- cyclohexanetriol
- axially chiral biaryl
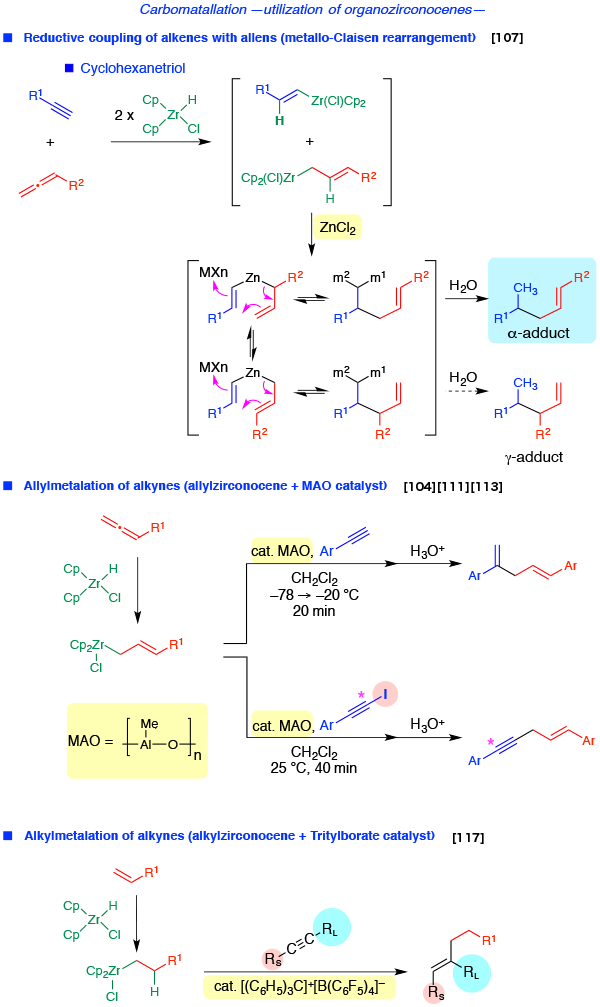
- Carbometalation using zirconocene reagent
- Reductive Coupling of alkenes with allens
- Allylmetalation of alkynes
- Alkylmetalation of alkynes
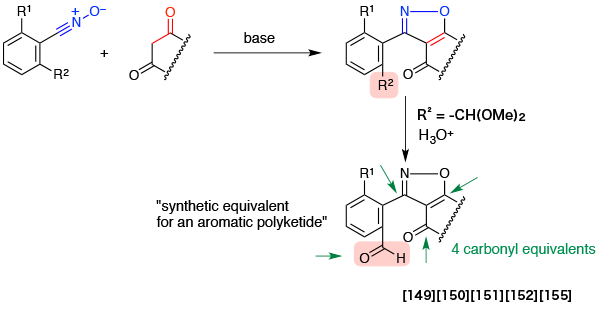
- Cyclocondensation of stable benzonitrile oxides with 1,3-diketones
- Aldehyde–ketone benzoin cyclization
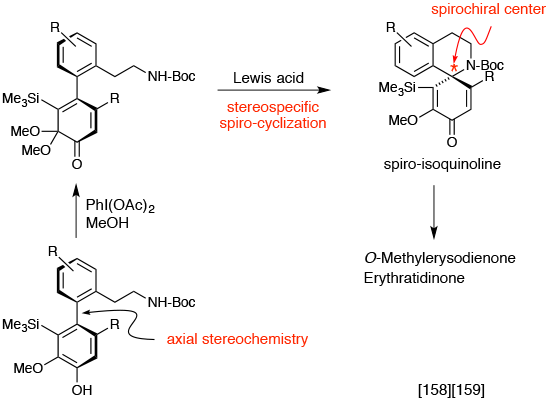
- Formation of spiroisoquinoline framework
Stereospecific 1,2-rearrangement
Highly efficient glycosidation (metallocene method)
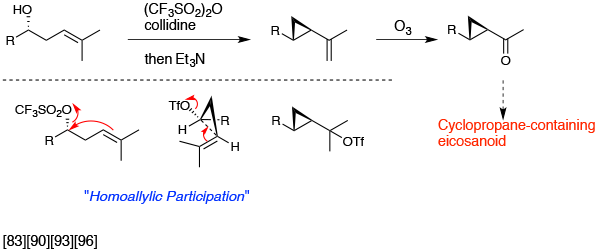
Cyclopropane formation
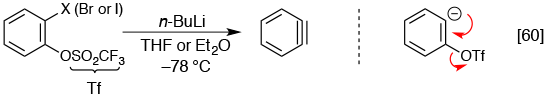
New efficient method for “benzyne
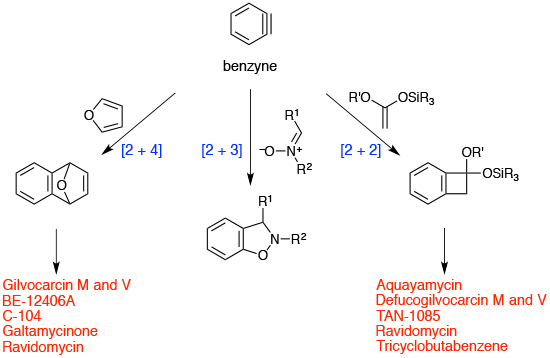
Cycloadditions of benzyne
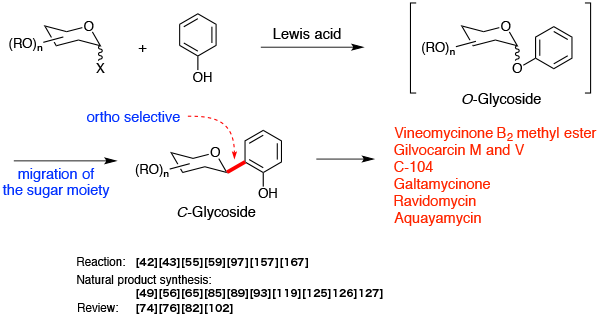
Aryl C-glycosidation reaction (O→C-glycoside rearrangement)
Chemistry of strained molecules 1
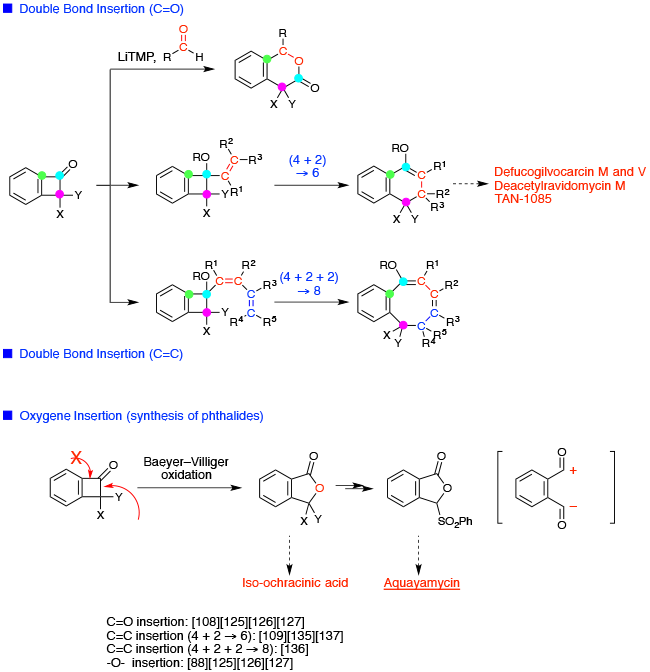
Chemistry of Strained molecules 2
Pinacol cyclization<
Group-selective hydroalumination
Chemistry of flavonoids
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Carbometalation using zirconocene reagent
Cyclocondensation of stable benzonitrile oxides with 1,3-diketones
Aldehyde–ketone benzoin cyclization
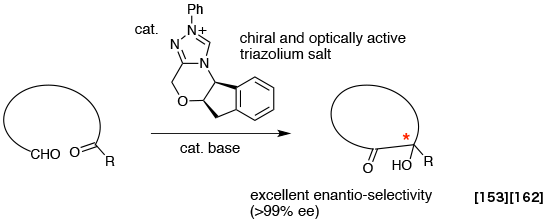
Formation of spiroisoquinoline framework